Connecting services
Services are a set of basic services provided to customers within the framework of the software functionality of the system. Each service acts as a separately charged entity with a charge for the amount of use. The system also implements the functionality of periodical services with a fixed write-off of funds for the period of use.
In order to switch to Services, you need to use the menu of your personal account, the “Customer” section.
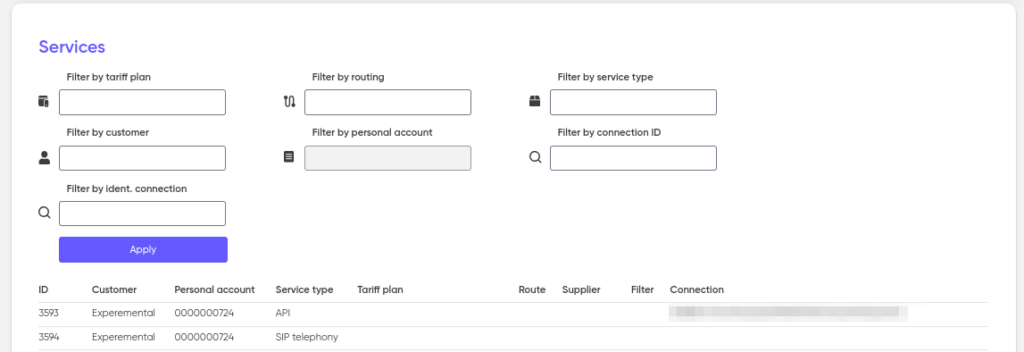
The “Services” section contains a list of all services currently connected to customers with the ability to switch to any service and add or change its settings.
The following types of services are implemented in the system:
| Type of service | Description |
|---|---|
| HLR | automatic anonymous check of subscribers’ availability without calling |
| SMS | mass SMS mailing of the lists of subscribers |
| SIP telephony | provision of telephone communication services over the SIP protocol |
| API | API request to activate the app that includes this service |
| TTS | speech synthesis service as part of the app |
| ASR | speech recognition service as part of the app |
| PUSH ID | secure authorization/registration of users online and offline |
Connecting a new service
In order to connect the service to the customer, go to his profile and open the “Personal accounts”. Then go to the personal account to which the new service will be linked or create a new one.

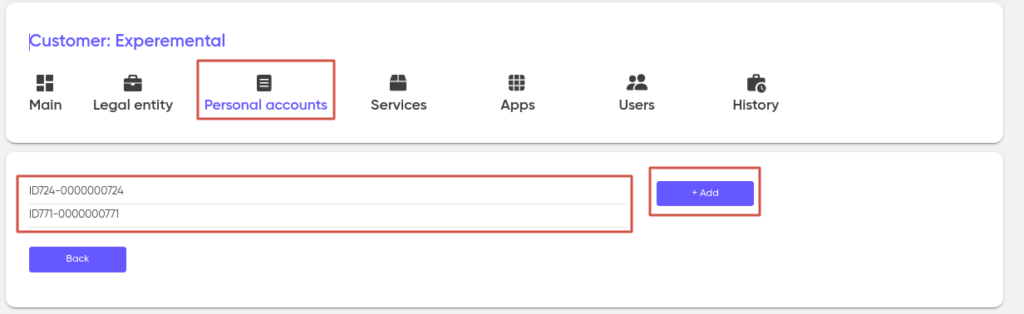
Next, in the Services section, click on “+ Add”.
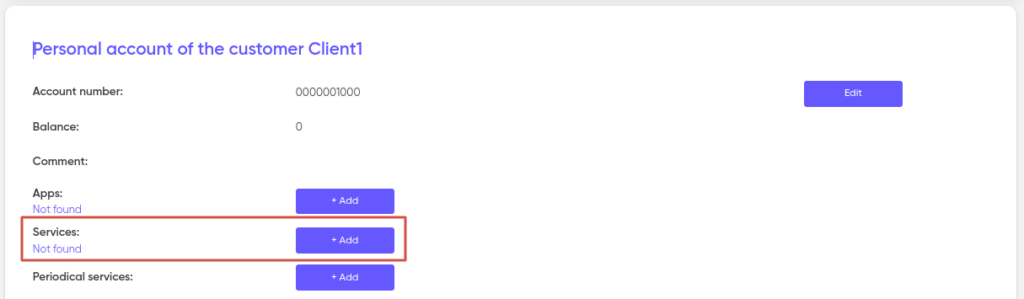
Select a new service from the “Service Type” drop-down list. After that, select a zero-cost tariff plan that corresponds to the type of service you selected. For example, for the type of IP telephony service, specify the tariff plan, in our example: “Zero cost (Call)”. Next, select the routing group. Then specify the Distribution Priority. High priority services will be served first.
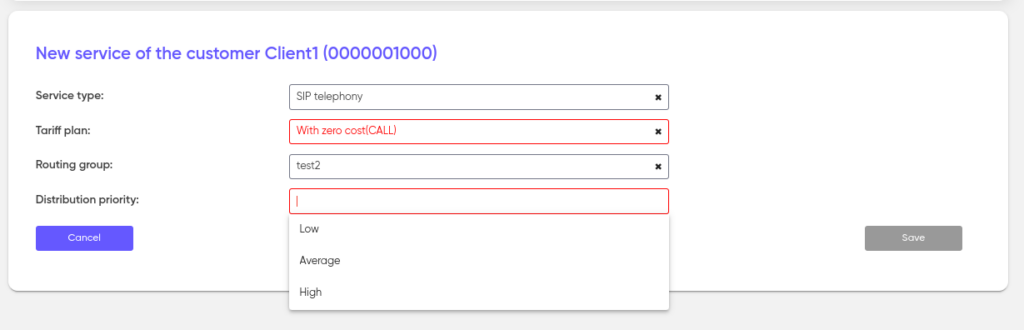
After completing all the settings, click “Save”. From this moment on, the new service has been created and linked to the personal account.
Please note that HLR services and Outgoing SMS become available for creating campaigns from your personal account.
Setting up a remote connection
The “Connections” section is used to configure access to services from external systems using various protocols. To add a new connection, go to the service and click on “+ Add”.
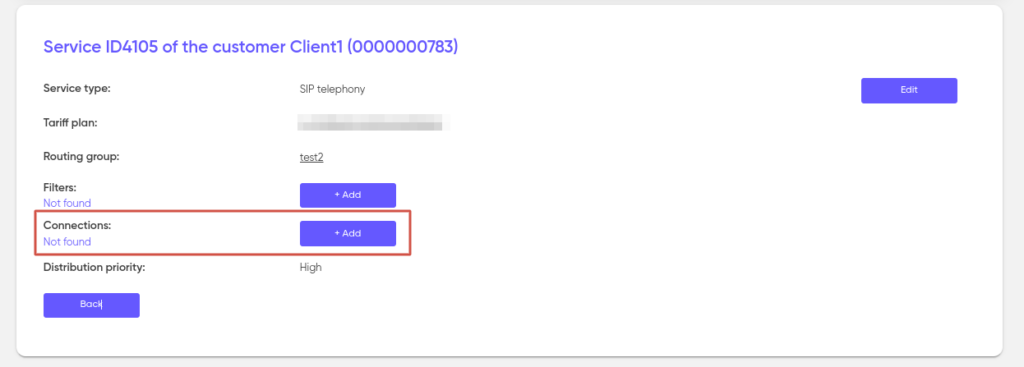
Table of supported protocols for different types of services:
| Service type | Supported transmission protocol |
|---|---|
| SIP telephony | SIP |
| API | SMPP, HTTP, Out HTTP (in development), IMAP, Telegram (in development) |
| PUSH ID | SMPP, HTTP |
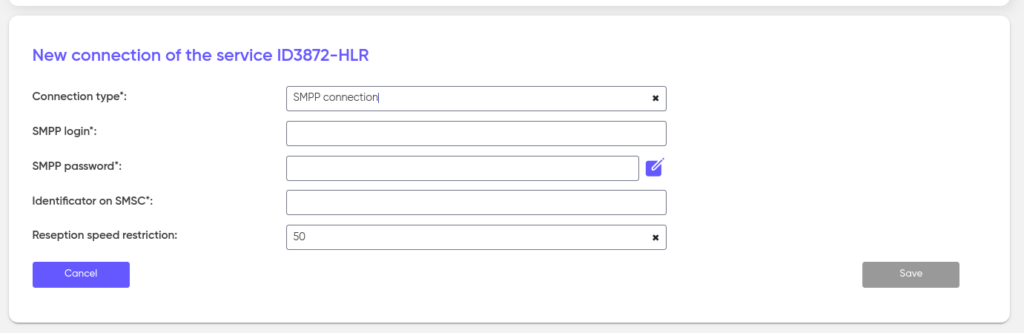
SMPP
Setting up SMPP transmission involves filling in two parameters: SMPP login and SMPP password. To create an SMPP login, use the Latin alphabet. Next, come up with a password in the same way or use the auto-generation function. After creation, the username and password are transmitted to the client.
To support older systems, it is possible to configure identification on the SMS center — the Identificator on SMSC. If it is not required, set the value to “0” (zero).
The SMPP protocol also implies the possibility of limiting the reception speed on links — Reception speed restriction. The default value is 50.
After completing the above procedures, click “Save”.
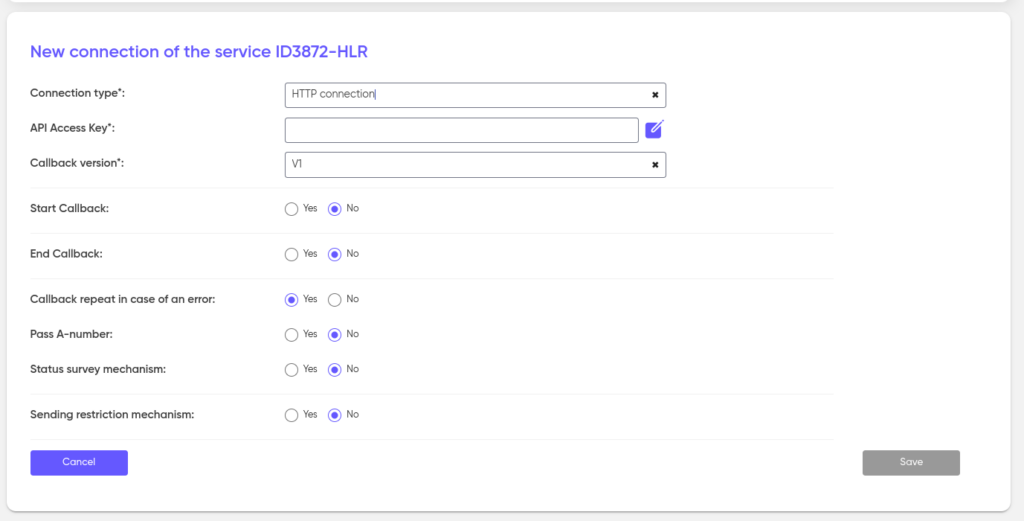
HTTP
HTTP transmission is configured as follows. Generate an API access key (it should be passed to the client). Next, install the Callback version (V1, V2 or V4), see the description in the Callback.
The Callback protocol implies the possibility of transmitting statuses. To transmit the start and end processing statuses, activate StartCallback and EndCallback. Specify the Transfer Method and address (URL). If the external system requires authorization, specify the Username and Password. Activating the CallbackRepeat setting in case of errors involves resending the callback status if an error occurred during the transmission of the status.
If you need to transfer an A-number, activate the appropriate setting — PassA-number.
When activating the “Status Survey Mechanism” setting, the external system will be polled, and the statuses coming from it will be recorded in the database of our system.
The sending restriction mechanism performs the function of anti-fraud. When this setting is activated, the number of shipments per number will be limited to the number that will be indicated in the Number of sendings field.
Save the settings you have made.
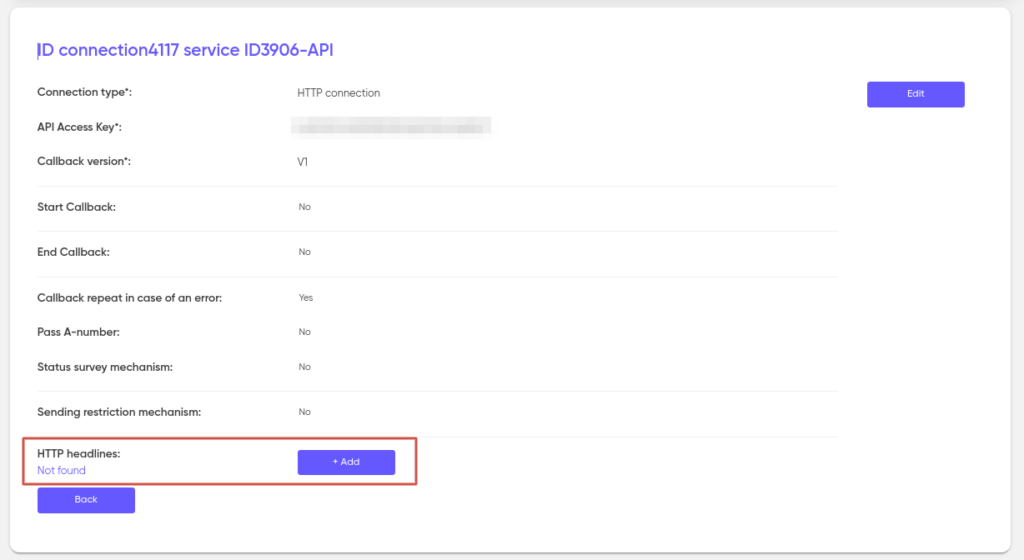
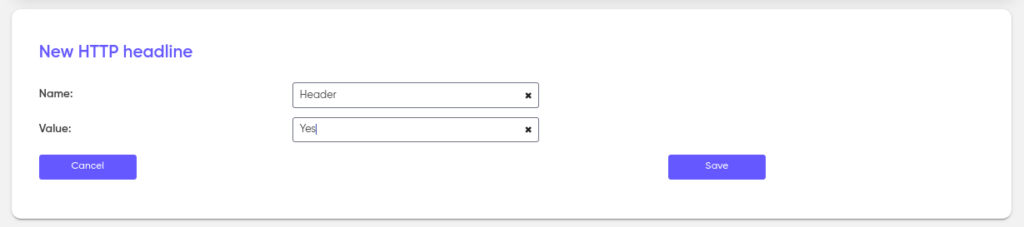
Please note that when transmitting an HTTP request in the callback exchange mechanism, we can add HTTP headers. To add an HTTP header, click add and specify an arbitrary name and value.
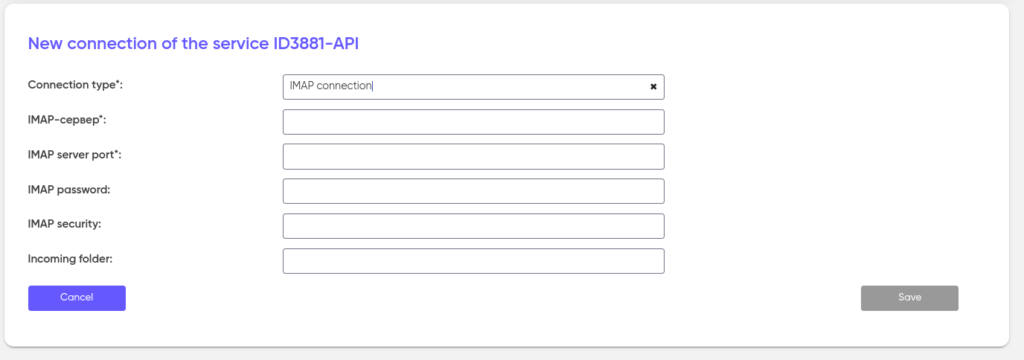
IMAP
E-mail access protocol. The way to activate the application using this protocol is a letter. To set up IMAP access, specify the IMAP-server, IMAP-port, and IMAPPassword. Next, select the IMAP protection method: No, SSL or STARTTLS and specify the Incomingfolder where the emails will be located (for example: INBOX).
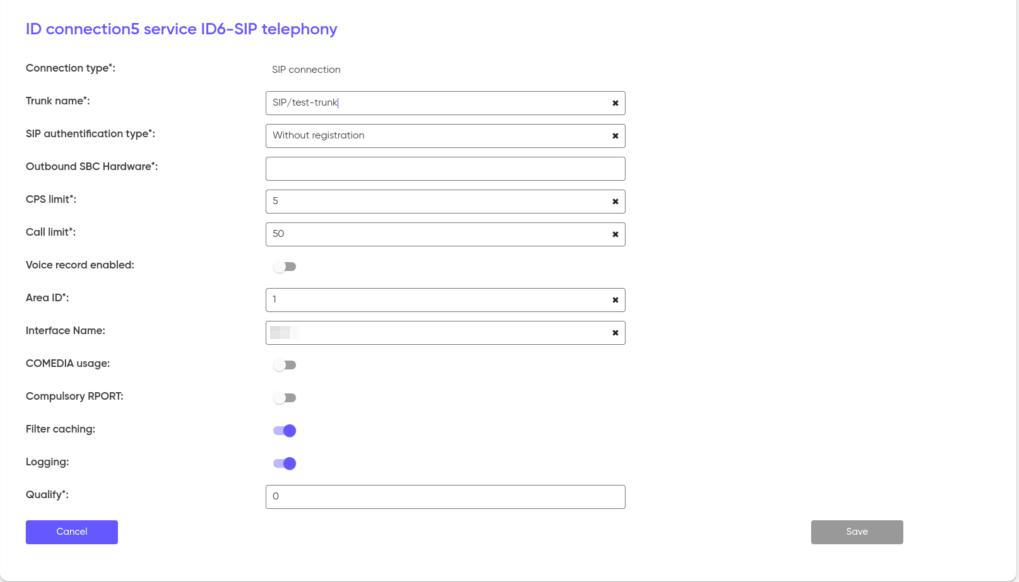
SIP
To set up a SIP connection, specify the TrunkName.
Depending on whether authentication is required on the trunk, select the appropriate type from the SIPAuthentication Type drop-down list. When selecting theRequireregistration with credentials type, enter the SipAuthUser — username and SipAuthPassword — password. If you select the Do Notrequireregistration type, select OutboundSBCHardware — the type of equipment that will serve the request direction.
Write down the CPSlimit — the limit on the number of simultaneous calls per line, and the Calllimit — the limit on the number of connecting lines.
Setting up Voicerecordenabled — activates the function of recording conversations from the trunk.
The AreaID field is always set to 1, and the InterfaceName field is set to unibell.
COMEDIA — ignores the data in the RTP headers and sends voice traffic to the source IP. It is used when the client’s hardware does not support NAT, but is located behind NAT. Activating the setting instructs the system to send a request not to the address specified in the packages, but to the one from which they come.
ForcedRPORT — adds the rport parameter to the header of SIP messages, which forces the remote server to send responses to the IP and port of the traffic source, and not what is specified in the Via messages.
Filtercaching — forces the platform to cache information about filters, rather than requesting it every time a call is made.
Logging — enabling the logging mechanism.
Qualiffy — the frequency of polling of the SIP device by the SBC for operation and availability for making a call. The value is indicated by a number (milliseconds). An OPTIONS message is sent. If the value 0 (zero) is specified in the line, the polling function is disabled.